What is actually meant by light pollution? If you ask yourself this question, you are absolutely right here! Whether through street lamps, in the apartment, or on luminous clams – for most people, the existence of artificial light sources is now a matter of course. Electric light ensures that we can see something in the dark. We also feel safer when we are traveling at night.
However, the earth is getting lighter, so there are fewer and fewer places that are completely dark. Unfortunately, only a few remember that the annually increasing light emissions have serious consequences for ourselves and for our environment.
In this article, I would therefore like to explain everything you need to know about so-called light pollution. From the definition, causes, and consequences to the solutions. Here we go!
- Definition
- Statistics
- Causes
- Consequences
- What to do?
- Final word
Definition: What is meant by light pollution?
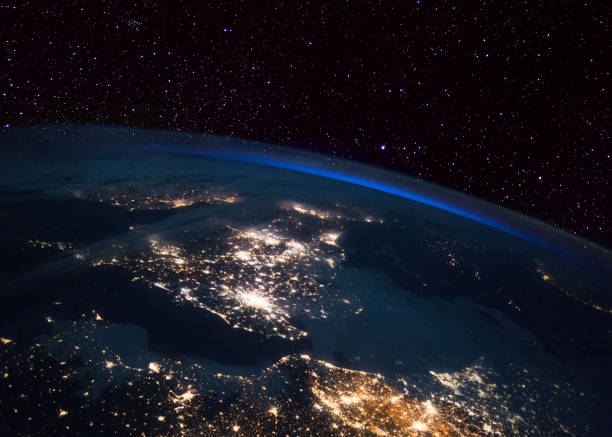

The concept of light pollution (also called light mug or light pollution) is the brightening of the night sky through artificial light sources, which in the regions concerned results in the absence of complete darkness. The light of electrical lighting is scattered into the atmosphere, which negatively influences the environment. This is also why light emissions are considered to be pollution from artificial light.
And what is natural light? This is, for example, the light of the sun and the stars – all the light that is not artificially generated by us humans.
Statistics: Which numbers and facts do there are light emissions and light emissions?
So we humans create a kind of “light waste”. But how bad is the problem really? In order to get a better understanding of this, I would like to give you some scientific numbers and facts about light pollution:
- Worldwide increase: The intensity of artificial lighting and the expansion of the illuminated area has increased by around 2 percent per year worldwide since 2012.
- Increase in the UK: according to estimates, light pollution in the UK increases by about six percent each year.
- Intensity: Our cities are sometimes 4,000 times brighter than the natural night light.
- Insect death: In one night, an average of 150 insects die on a single street lamp. According to the Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection, there are around ten million lanterns.
- Distribution: More than 80 percent of the world’s population and more than 99 percent of the US and European populations live under a light-dirty sky.
Causes: How is light pollution?

Through human influence, the earth is not only warmer (keyword climate change), but also even brighter. But how exactly do we cause light emissions? The answer to this question could be an infinite list of light sources – I would like to save you. Instead, I present the most important causes of the increasing light mug here.
Technical progress
Electrical lighting is becoming increasingly effective so that a lot more light can be generated with the same electricity. The lower power consumption means that even more or even lighter lighting is installed. (Rebound effect)
Bad light distribution
Most of the time, light sources are not well shielded, so they not only lighten the object to be illuminated or the environment to be illuminated, but also seem uncoordinated in all directions. Also where no light is needed.
Conspicuous advertising technology
Advertising has to stand out. Therefore, more and more digital advertising displays, illuminated clams, showcases, and City Light posters are illuminating the cities. Spectacular light pigs and projections are also used (for example at festivals).
Expansion of residential areas and infrastructure
In new residential areas, not only the houses and apartments but also the installation of further street lamps and floodlight systems provide additional light – in places where it was still quite dark. The expansion of industrial areas also requires corresponding, new lighting.
Road traffic
It is not only the street lamps that lighten the planet in the dark but above all the headlights and lighting of our vehicles.
Read Also: Air Pollution In Chicago Area Impacts Communities Of Color The Most
Decoration
Especially in the Christmas season, the houses, streets, and cities shine particularly brightly, since the Christmas decoration is brought out of the basement with all the light curtains, fairy lights, and illuminated figures.
Do you think of other causes of light emissions? Then please write me a comment with your hint.
Follow: How does light pollution affect us humans and the environment?

Apart from the fact that the lighting of streets, buildings, and advertising displays needs tons of energy – how does it affect the environment when the nights are no longer dark? And to what extent do we humans even do ourselves with it?
Here I will now introduce you to the essential consequences of light pollution.
Follow for animals
In the dark, nocturnal insects are based on the weak light of the stars. However, since the animals are now attracted to the much more intense, artificial light of the street lighting or buildings, they leave their usual habitats. They either burn up on the hot lights, wandering to exhaustion around them, and are generally concentrated, as on the silver tray, a slight prey for insect eaters. This is also why light pollution is considered one of the main causes of insect death.
Ships, bridges, or bridges are often heavily illuminated, which also affects the underwater world. For example, fish such as salmon or eels are disturbed by light sources during their spawning hikes. In addition, the light of the port cities also irritates sea turtles.
Migratory birds are also disturbed by the nightly, artificial lighting so that they fly other routes and lose a lot of strength. Last but not least, light even has an impact on the mating behavior of many animal species.
Consequences for plants
The chronobiological rhythm of plants is also influenced by increasing light emissions. Your natural growth cycle is disturbed, so you are more susceptible to weather damage, for example. This in turn has other negative consequences for the animal world.
Consequences for us humans
Our day-night rhythm comes through the artificial light. As a result, for example, we can fall asleep much worse. Usually, our body pours out the sleep hormone melatonin in the dark – the lighter it is, the less can be produced and the worse sleep.
Our internal clock no longer works as usual. This has health consequences because it primarily affects our well-being, our relaxation, and our ability to concentrate.
Tip: To sleep better, you should sleep in complete darkness and sit in front of the flickering television in a completely illuminated apartment.
Have you ever wondered why you hardly see any stars in the big city at night? There is a large, artificial light bell in natural darkness in cities such as Cologne, Berlin, Munich, or Hamburg. This light pollution ensures that only a small fraction, which is about 3,000 – 4,000 stars recognizable in complete darkness.
Solutions: What can each of us do against light pollution?

Basically, you can stop air pollution by turning off the artificial light. Relatively logical, right? However, we humans cannot just live in complete darkness overnight. Nevertheless, there are some tips that everyone can really implement to significantly reduce their own light emissions:
- Switch off: actively switch off light sources if you don’t necessarily need them. So you can also save costs for energy.
- Automatic light: Use timing and motion detectors to ensure that lamps and lights are out if nobody needs them.
- Distribution down: Dear lights as low as possible and downwards so that you only illuminate the areas in which the light is required. The lighting upwards is rarely necessary. Above all, try not to illuminate trees and shrubs.
- Insect-friendly lamps: Make sure that the blue shares in the light are negligible or not at all existent.
- Lamp housing: Make sure that lights in the garden or at the house are surrounded by housing and cannot become hotter than 60 degrees.
- Promote star protection areas: There is no light in selected locations. For example, the Eifel National Park is considered a star protection area. Support them and the creation of further such star parks.
- Report light sources: Often street lamps are not covered upwards or are fundamentally much too bright. Look for such observations at the municipal utilities in your region in order to initiate a possible improvement.
- Earth Night: Take the annual environmental protection campaign every year, in which all lights in your own four walls will be switched off from 10 p.m. at the latest.
Light pollution – a man-made problem for people and the environment
Fortunately, in everyday or public discussions, one now very often talks about the environmental problems of our time. However, light pollution is still rare. It is important that this changes and that we take the problem seriously. Because the bright light in the dark has serious consequences for the animal world, for plants, and, above all, for ourselves.
Let us learn to live with as little electrical light as necessary – and to get up with the sunrise if possible and go to sleep with the sunset. This is by far the best remedy for light emissions.
I hope that this article has opened a light. Have you had any questions, suggestions, or your own experiences with light pollution that you want to share? I’m looking forward to your comment.
Stay sustainable,